How Multimodal AI is Transforming Developer Workflows in 2026

Written by
Tarun Malik
Front End Developer
Keshav Saini
Front End Developer
Table of contents
Build with Radial Code
The year 2025 marks a new era for developers — one where multimodal AI isn’t just an assistant but a true collaborator. Gone are the days when AI could only handle text-based prompts or code completions. Today, developers interact with intelligent systems that can see, hear, understand, and generate across multiple data types — from text and code to images, audio, and even real-time video.
This evolution is radically reshaping how developers build, debug, and deliver software. Let’s explore how multimodal AI is transforming developer workflows in 2025. Learn how top developers are using multimodal AI to innovate faster — explore more on our website.
Unified Development Through Multimodal Inputs
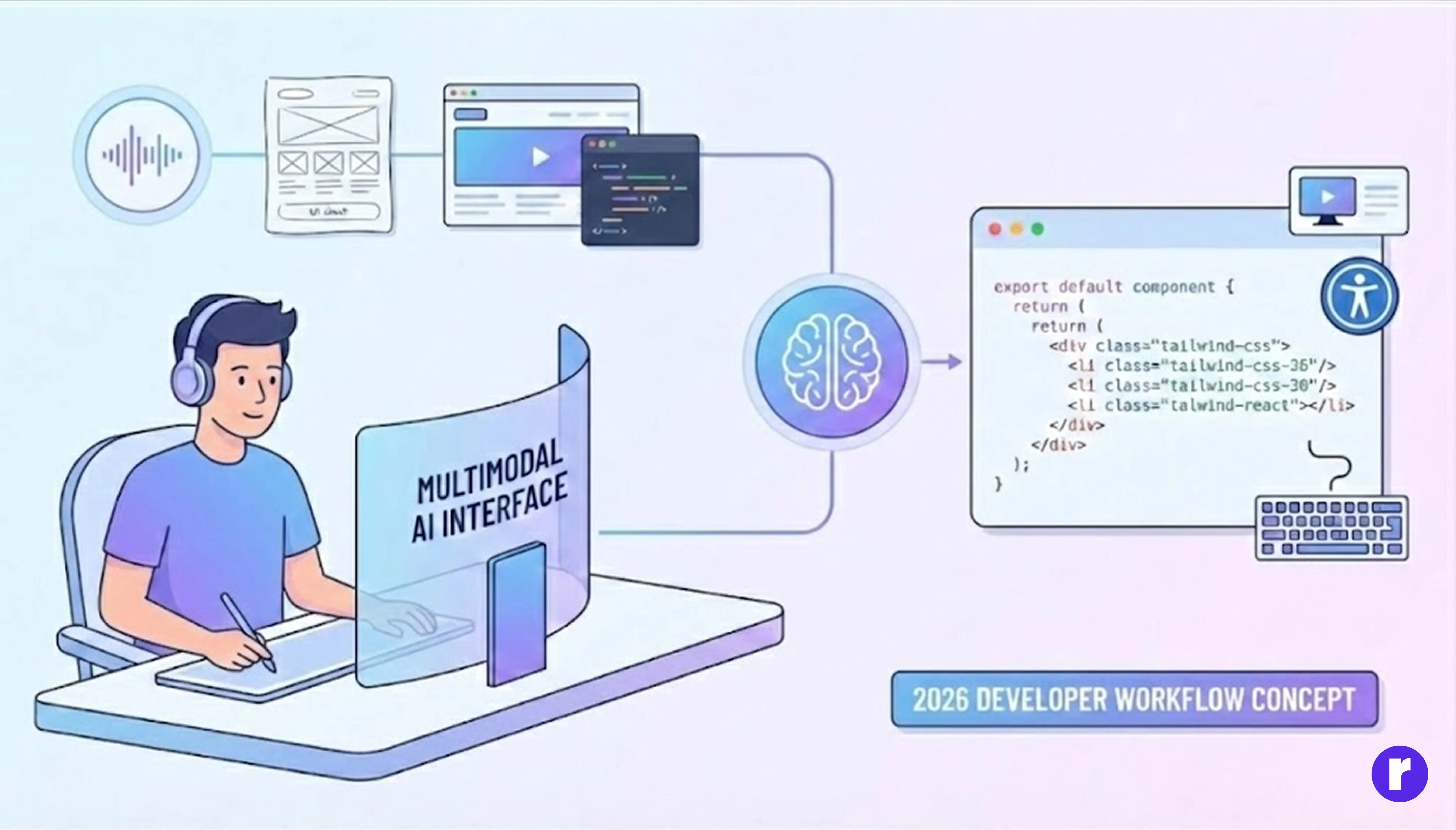
Traditional AI assistants relied heavily on text prompts. In 2025, multimodal systems enable developers to combine voice commands, sketches, screenshots, and code snippets in a single interaction.
Imagine describing a UI verbally, uploading a wireframe, and watching the AI generate a complete React component — styled with Tailwind CSS and optimized for accessibility.
This shift eliminates the friction between idea and implementation. Developers no longer need to switch tools or context; AI bridges the gap between design, code, and documentation. Continue your learning journey at Radial Code.
Smarter Debugging with Visual and Contextual Awareness
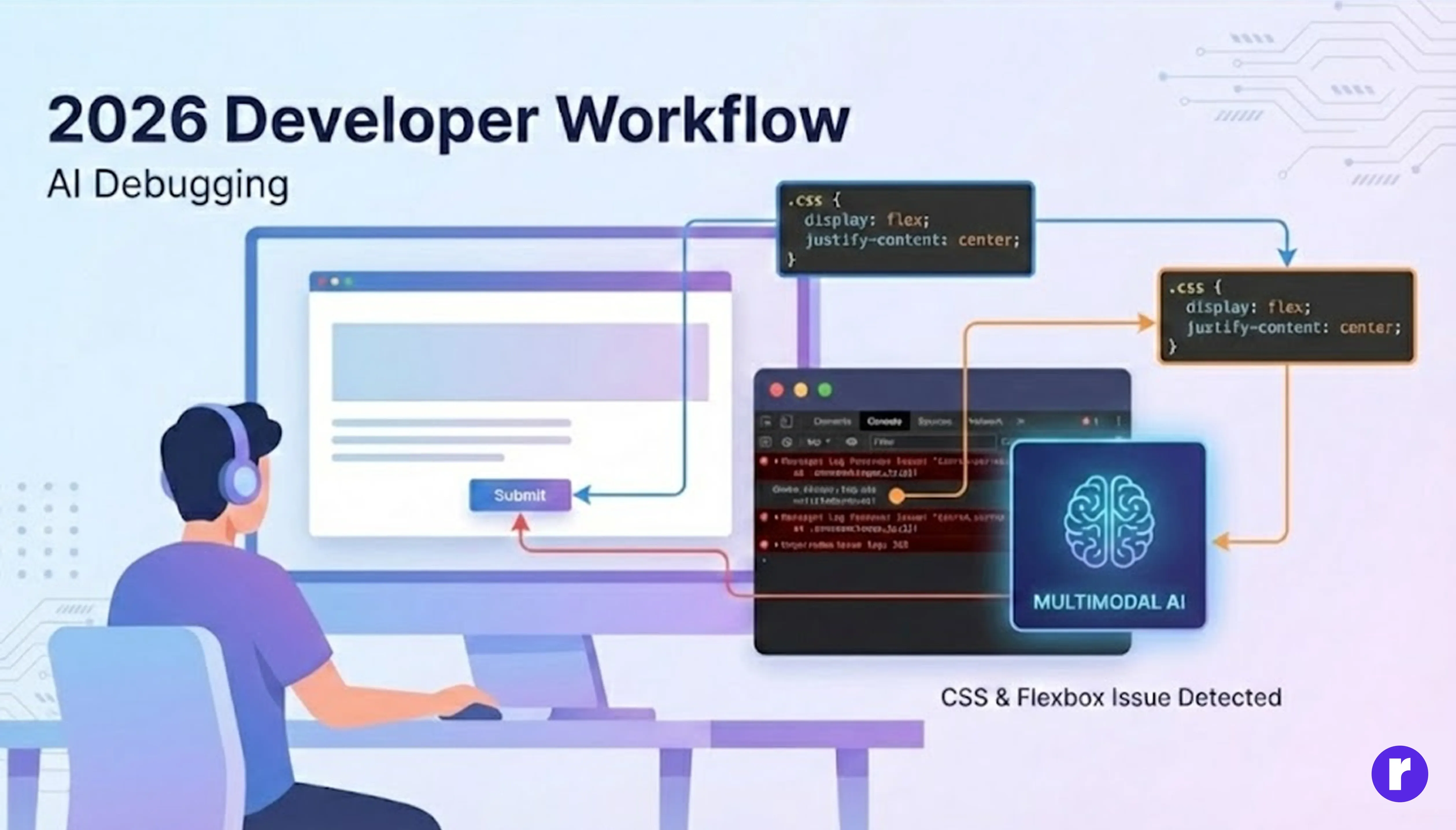
Debugging is no longer about staring at cryptic console errors. With multimodal AI, developers can upload screenshots or screen recordings of a bug, and the AI instantly identifies the issue by analyzing both visual and textual context.
For example:- An AI might detect that a misaligned button in a web app stems from a missing CSS property or an incorrect flex setting. It can then suggest — or even apply — the fix directly in the codebase.
This visual debugging capability saves countless hours, especially in front-end and UI-heavy projects.
Real-Time Collaboration with Multimodal Agents
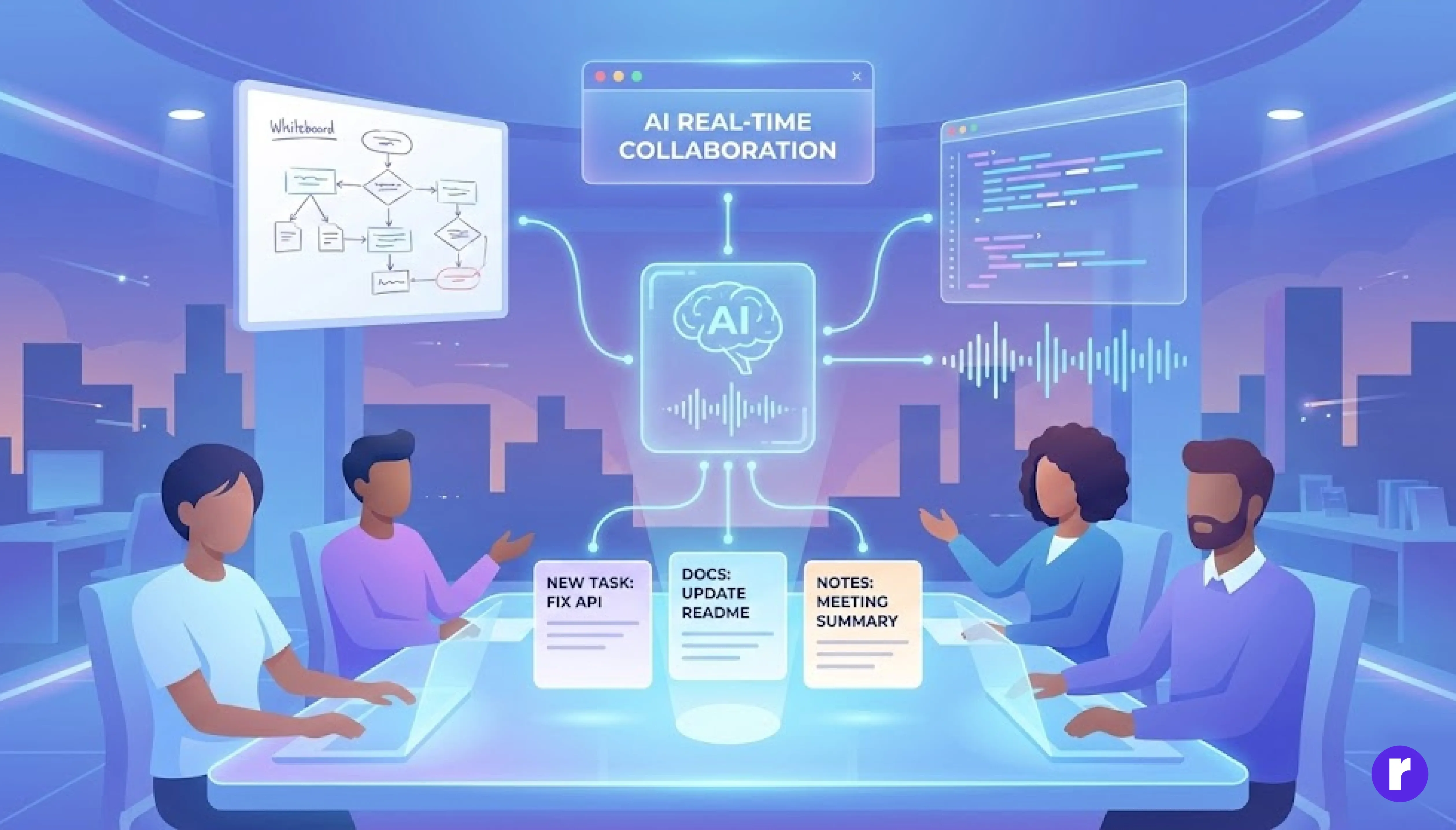
In 2025, multimodal AI agents work alongside developers as active team members. They can join meetings, listen to conversations, and interpret things like whiteboard sketches or code screenshots. If a developer uploads an audio note or a picture of code, the AI can understand it and update documentation or create tasks automatically.
These agents don’t just record information—they understand the intent behind what’s being discussed. For example, if someone suggests a new feature during a meeting, the AI can create a task for it and assign it to the right person. After meetings, the AI summarizes key points and next steps, helping everyone stay on track. This makes collaboration faster, reduces manual work, and ensures nothing important is missed.
Accelerated Prototyping and Design-to-Code Automation
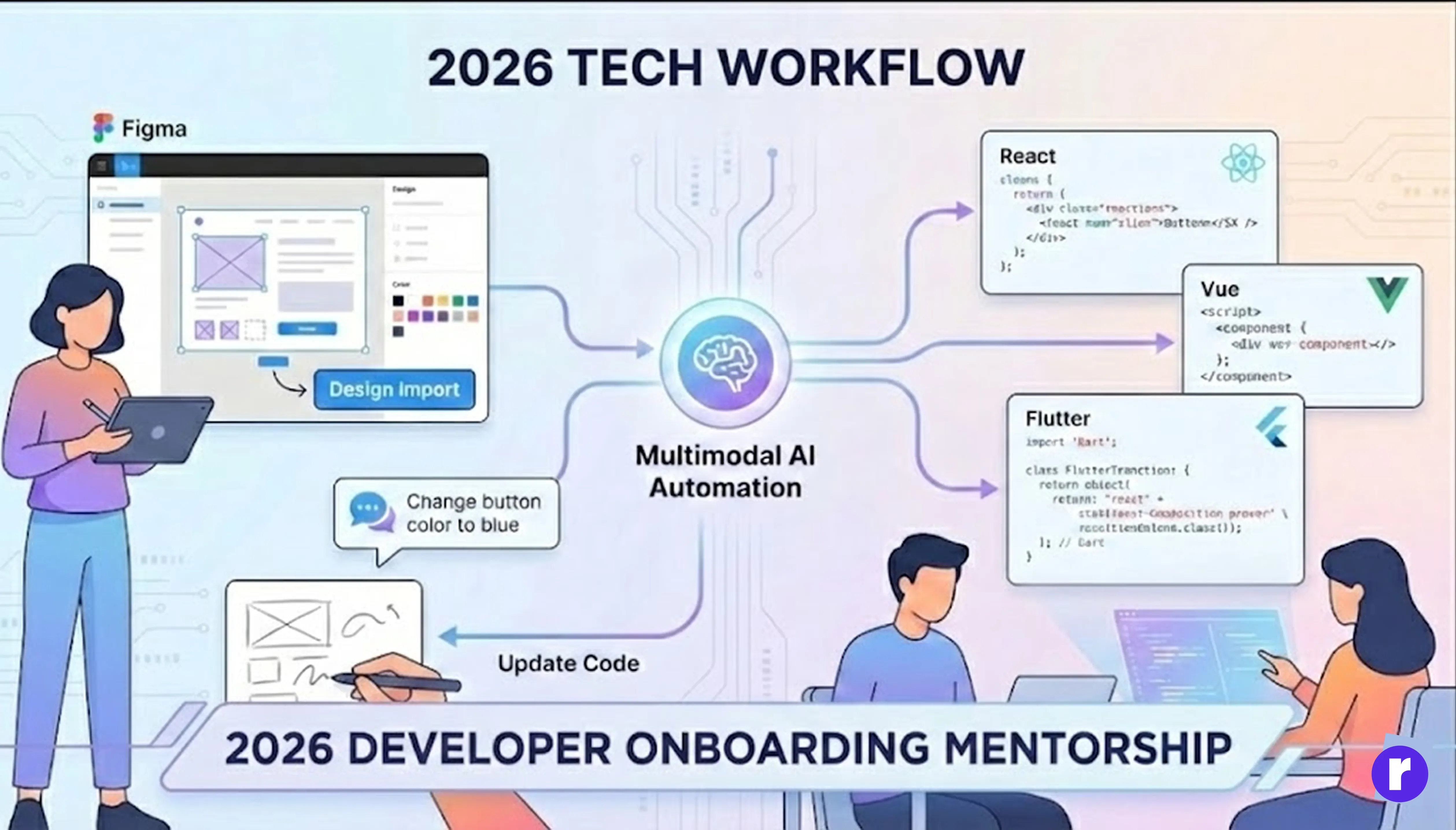
Multimodal AI has made design-to-code automation seamless. Developers can import a Figma or Photoshop design, and AI translates it into clean, production-ready code in frameworks like React, Vue, or Flutter.
Even more impressive, developers can adjust the design using natural language or by sketching directly over the interface. The AI interprets those changes and updates the code instantly — bridging the gap between designers and developers.
Enhanced Learning and Onboarding
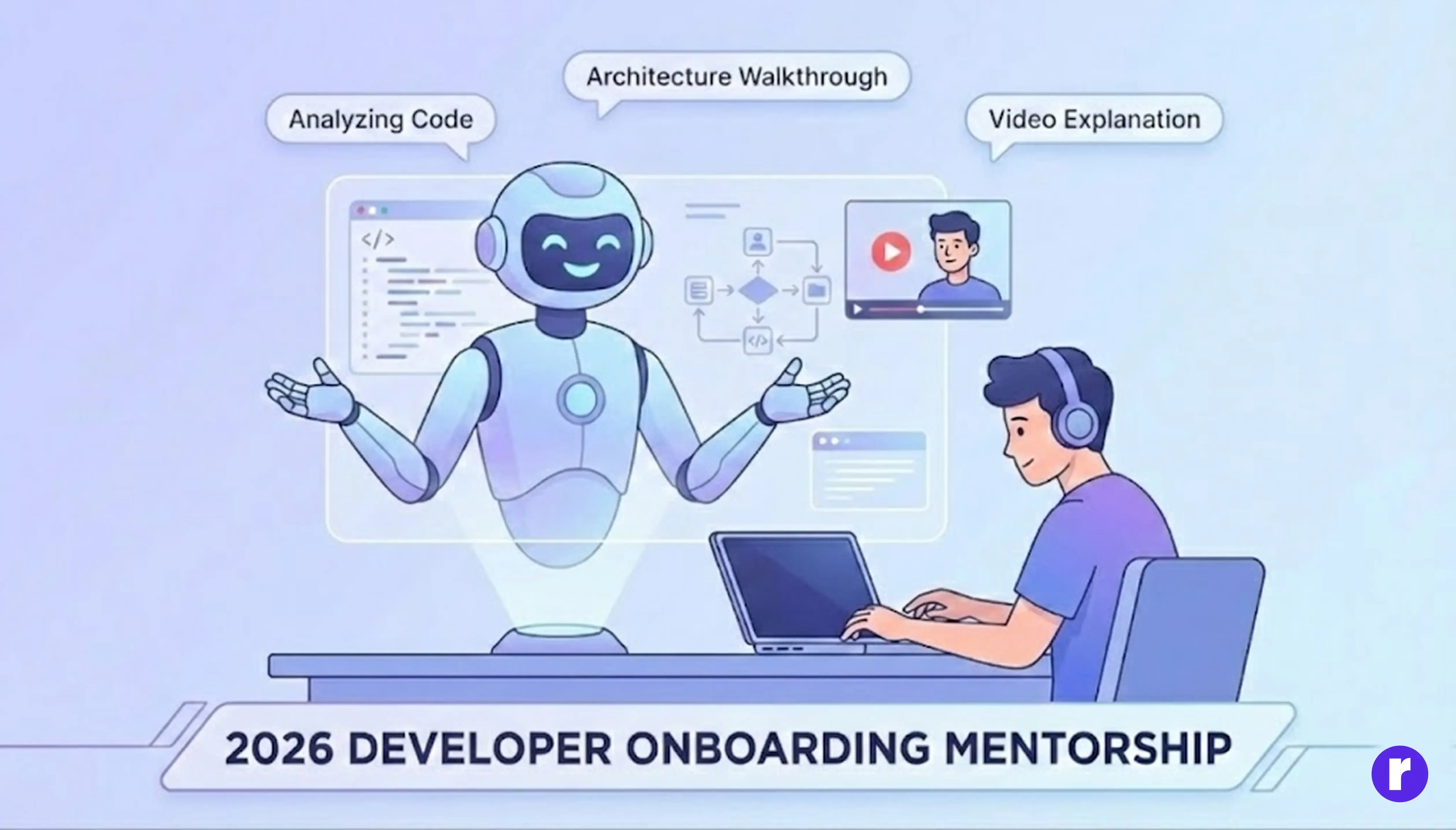
For new developers, multimodal AI serves as a personalized mentor. It can analyze a developer’s coding style, suggest improvements, and even provide video walkthroughs of complex concepts.
New team members can upload snippets of legacy code, and the AI will visually explain dependencies, architecture, and logic flow — turning steep learning curves into interactive learning experiences.
Code Review Reimagined
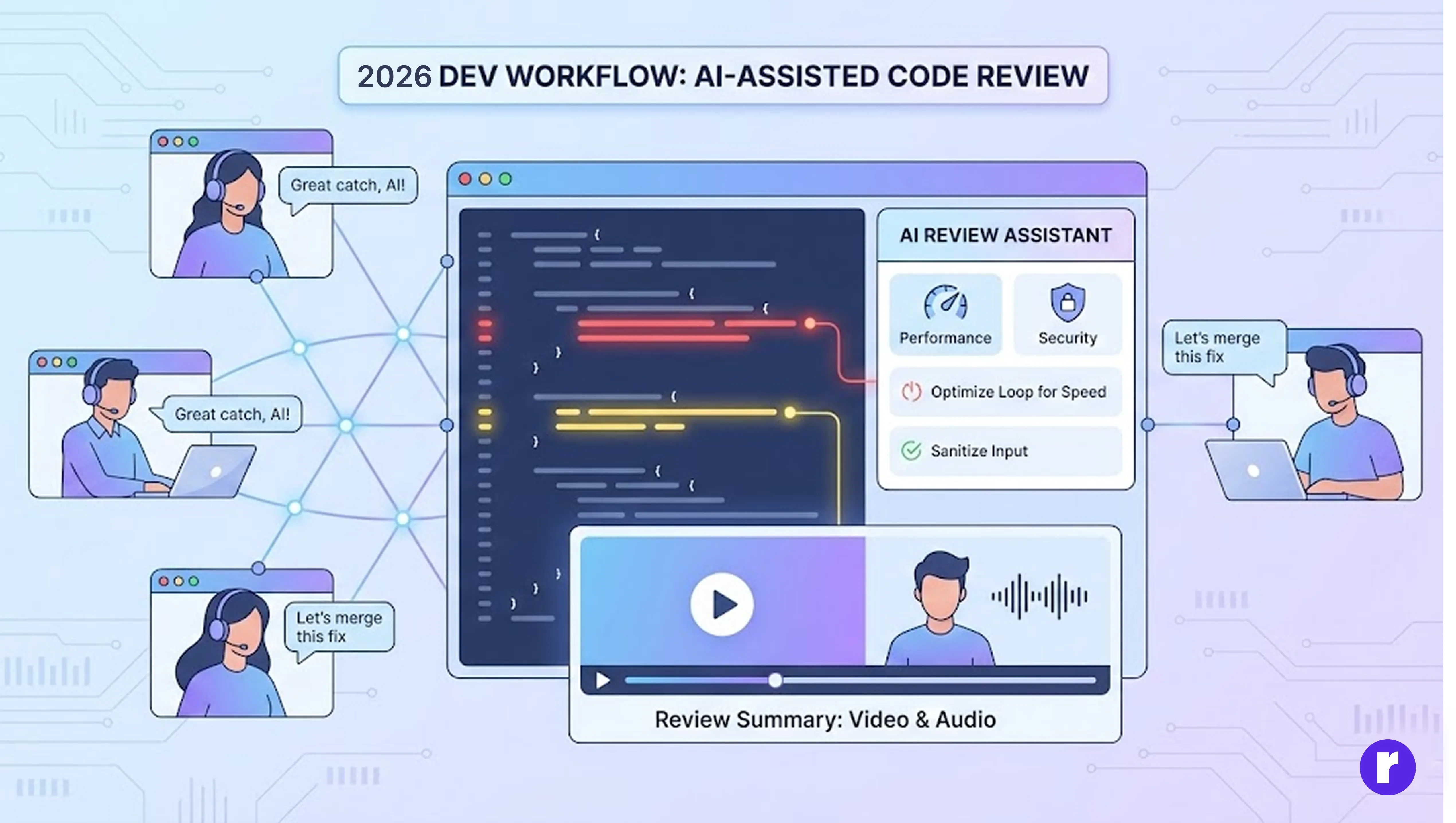
Modern code reviews are now AI-assisted and context-rich. Instead of static comments, multimodal AI tools can record video summaries of review sessions, highlight problematic code areas visually, and suggest performance or security optimizations.
This makes collaboration between remote teams faster and more human-centered, removing misunderstandings that often arise from text-only feedback.
- AI-Assisted Reviews: The AI can automatically scan code for bugs, security issues, or performance problems, and suggest improvements. This speeds up the review process and helps catch issues that might be missed by humans.
- Context-Rich Feedback: Instead of just text comments, AI tools can create video or audio summaries of the review, visually highlight the exact lines or sections of code that need attention, and even provide side-by-side comparisons of before-and-after changes
The Rise of Multimodal DevOps

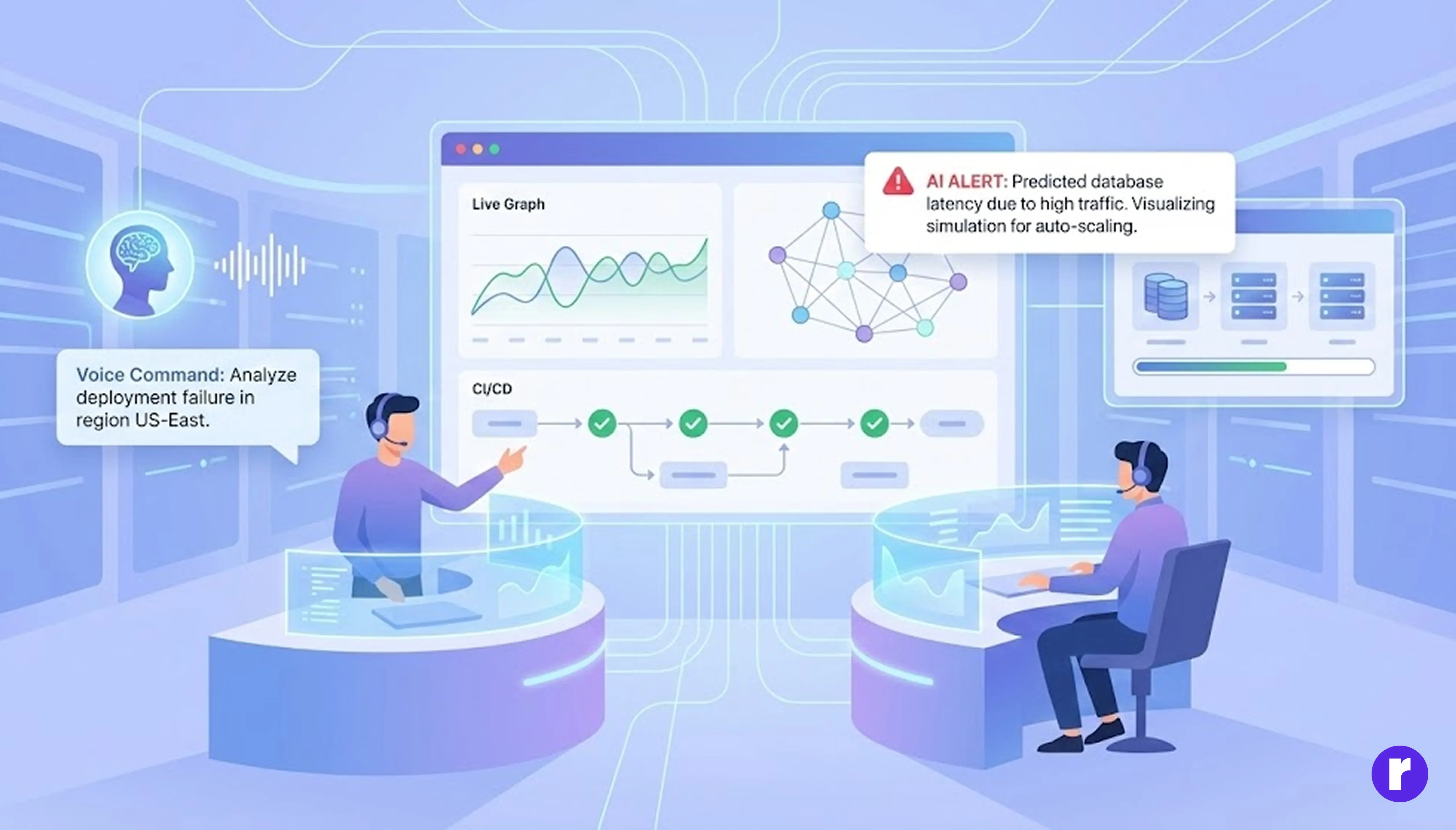
Even DevOps workflows have evolved. Engineers can now use dashboards that integrate natural language queries, system visuals, and live metrics. An AI system can visually explain deployment issues, analyze error logs, and even simulate different infrastructure configurations through interactive graphs.
This holistic understanding enables teams to predict issues before they happen and maintain smoother CI/CD pipelines.
- Unified Dashboards: Engineers can interact with dashboards using natural language (typing or speaking questions), view system diagrams, and monitor live performance metrics all in one place. This makes it easier to get a complete picture of the system’s health and status.
- AI Explanations: When something goes wrong (like a failed deployment), the AI can analyze error logs and system visuals, then explain the issue in simple terms. For example, it might highlight a problem area in a network diagram and describe what caused the failure.
- Simulations: AI can create interactive graphs to simulate changes in infrastructure. Teams can see the potential impact of adding new servers, changing configurations, or updating software before making those changes live.
- Proactive Problem Solving: By combining all this information, AI can spot patterns and predict issues before they cause real problems. For example, it might notice a trend in error logs that usually leads to downtime and alert the team early.
- Smoother CI/CD Pipelines: All these capabilities help teams automate and streamline their continuous integration and deployment processes, reducing errors and speeding up software releases.
Ethical and Responsible AI Development
As multimodal AI becomes deeply embedded in development workflows, the focus on responsible and transparent AI has intensified. Developers now rely on built-in explainability tools that show why an AI suggested a particular change or recommendation.
This transparency ensures that human oversight remains central, promoting ethical innovation across industries.
- Responsible: AI should be designed and used in ways that are fair, unbiased, and respect user privacy. Developers must ensure that AI does not cause harm or make decisions that could negatively impact people or organizations.
- Transparent: Modern AI tools now include features that explain their suggestions or actions. For example, if an AI recommends a code change, it also shows the reasoning behind that suggestion. This helps users understand and trust the AI’s decisions.
- Human-Centered: Even with advanced AI, humans remain in control. Developers can review, accept, or reject AI recommendations. This keeps human judgment at the center of the workflow.
- Promoting Ethical Innovation: By focusing on transparency and responsibility, organizations can innovate with AI while ensuring their solutions are ethical and trustworthy across different industries.
Conclusion
In 2025, multimodal AI is not replacing developers — it’s amplifying their capabilities. By understanding not just code, but also images, audio, and context, AI is turning software development into a more intuitive, visual, and creative process. The next phase of innovation won’t just be about writing better code — it’ll be about designing smarter, communicating seamlessly, and collaborating with intelligent systems that understand the full spectrum of human expression.
