Understanding Nuxt Pages, Layouts, and Components

Written by
Ankit Godara
Front End Developer
Vishal Chanda
Front End Developer
Table of contents
Build with Radial Code
In modern web development, building scalable and maintainable applications is essential. Nuxt.js, a powerful framework built on top of Vue.js, offers a highly structured yet flexible approach to web application development with minimal configuration.
One key reason for Nuxt's popularity is its opinionated architecture centered around three core building blocks:
- Pages
- Layouts
- Components
Understanding these elements individually and together improves your development workflow, resulting in cleaner code and easier maintenance.
In this blog, we dive deep into these core concepts, explore their differences, use cases, best practices, and practical examples.
What is Nuxt.js?

Nuxt.js simplifies development of:
- Universal (Server-Side Rendered) applications
- Static-generated applications
- Single-page Vue applications
It comes with built-in features such as:
- A file-based routing system
- A layout system
- Server-side rendering out of the box
Instead of manual route setup, Nuxt leverages project file structure for minimal configuration, making development faster, organized, and SEO-friendly.
Want to learn more click here
Nuxt Pages: The Entry Points of Your Application
In Nuxt.js, pages represent the core views of your application. Each .vue file inside the pages/ directory automatically becomes a route, thanks to Nuxt's file-based routing system.
How Pages Work
When you create .vue files inside the pages/ directory, Nuxt converts them into URLs. For example: pages/
├── index.vue
├── about.vue
└── blog/
├── index.vue
└── [slug].vue
Nuxt interprets these files as:
- index.vue → / (homepage)
- about.vue → /about
- blog/index.vue → /blog
- blog/[slug].vue → /blog/:slug (dynamic route)
This system eliminates the need for manual route configuration, reducing boilerplate code and potential errors.
Benefits of Nuxt Pages
- Automatic Routing: Routes are created automatically from your file structure.
- Dynamic Pages: Easily create dynamic routes using square brackets [param] syntax.
- SEO-Friendly: Supports server-side rendering and static site generation for better SEO.
- Easy Maintenance: Each page is isolated, making large applications easier to manage.
Example: A Simple Nuxt Page
<!-- pages/about.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>About Us</h1>
<p>Welcome to our Nuxt.js application!</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "AboutPage",
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
color: #2c3e50;
}
</style>
This page will automatically be available at http://localhost:3000/about
Nuxt Layouts: Structuring Your Application
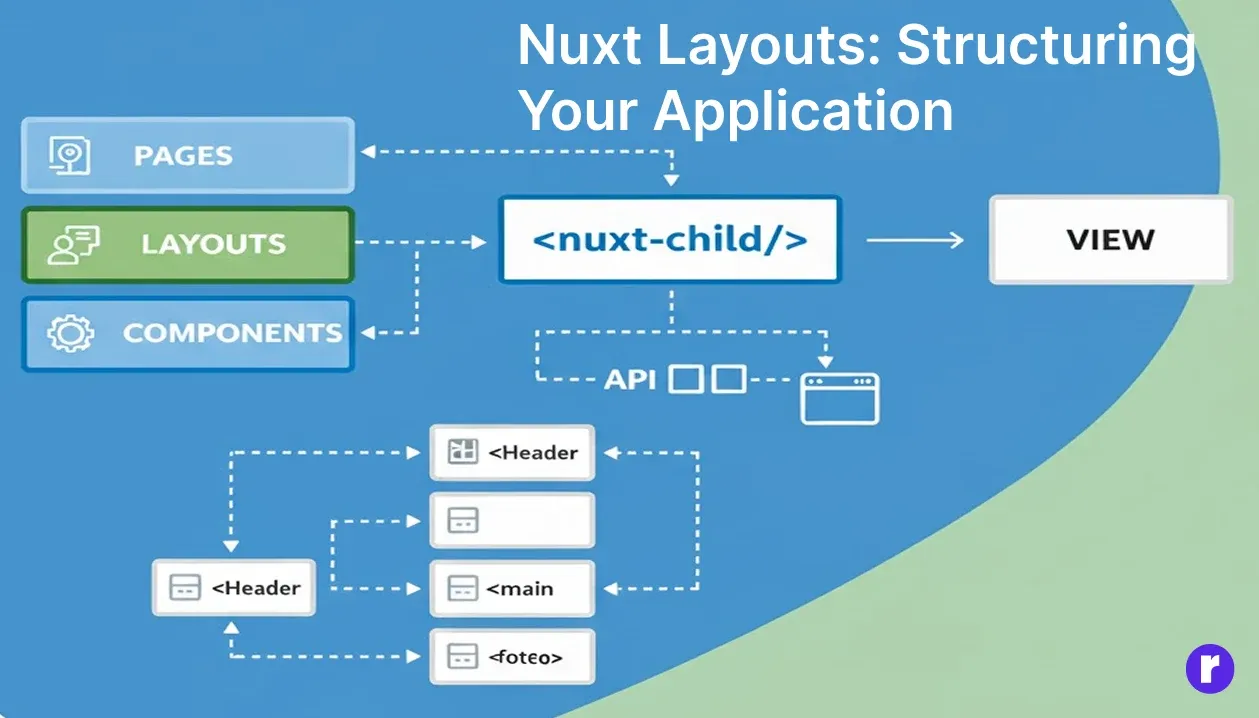
While pages define the content of your application, layouts define the structure. Layouts act as templates that wrap around your pages, allowing you to maintain a consistent structure across multiple pages without repeating code.
Default Layout
Nuxt provides a default layout at layouts/default.vue. This layout is automatically applied to all pages unless a custom layout is specified.
Example:-
<!-- layouts/default.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<header>
<nav>
<nuxt-link to="/">Home</nuxt-link>
<nuxt-link to="/about">About</nuxt-link>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<Nuxt />
</main>
<footer>
<p>© 2025 My Nuxt App</p>
</footer>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
header {
background-color: #f8f8f8;
padding: 1rem;
}
footer {
text-align: center;
padding: 1rem;
}
</style>
Note the Nuxt component: it is a placeholder where the page content is rendered.
Creating Multiple Layouts
You can create multiple layouts by adding Vue files in the layouts/ directory: layouts/
├── default.vue
└── admin.vueTo use a custom layout (e.g., admin.vue) for a page, specify the layout property in the page component:
<!-- pages/admin.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>Admin Dashboard</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
layout: "admin",
}
</script>This tells Nuxt to use layouts/admin.vue instead of the default layout for /admin.
Benefits of Using Layouts
- Consistent UI: Reuse headers, footers, or sidebars across multiple pages easily.
- Separation of Concerns: Keeps structural code (layout) separated from page-specific logic.
- Flexibility: Different sections of your app can have their own distinct layouts (e.g., landing pages, dashboards, auth pages).
Example of a Custom Admin Layout
<!-- layouts/admin.vue -->
<template>
<div class="admin-layout">
<aside>
<AdminSidebar />
</aside>
<main>
<Nuxt />
</main>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import AdminSidebar from '~/components/AdminSidebar.vue'
</script>
<style scoped>
.admin-layout {
display: flex;
min-height: 100vh;
}
aside {
width: 250px;
background-color: #1e293b;
color: white;
}
main {
flex: 1;
padding: 2rem;
}
</style>
Nuxt Components: Reusable Building Blocks
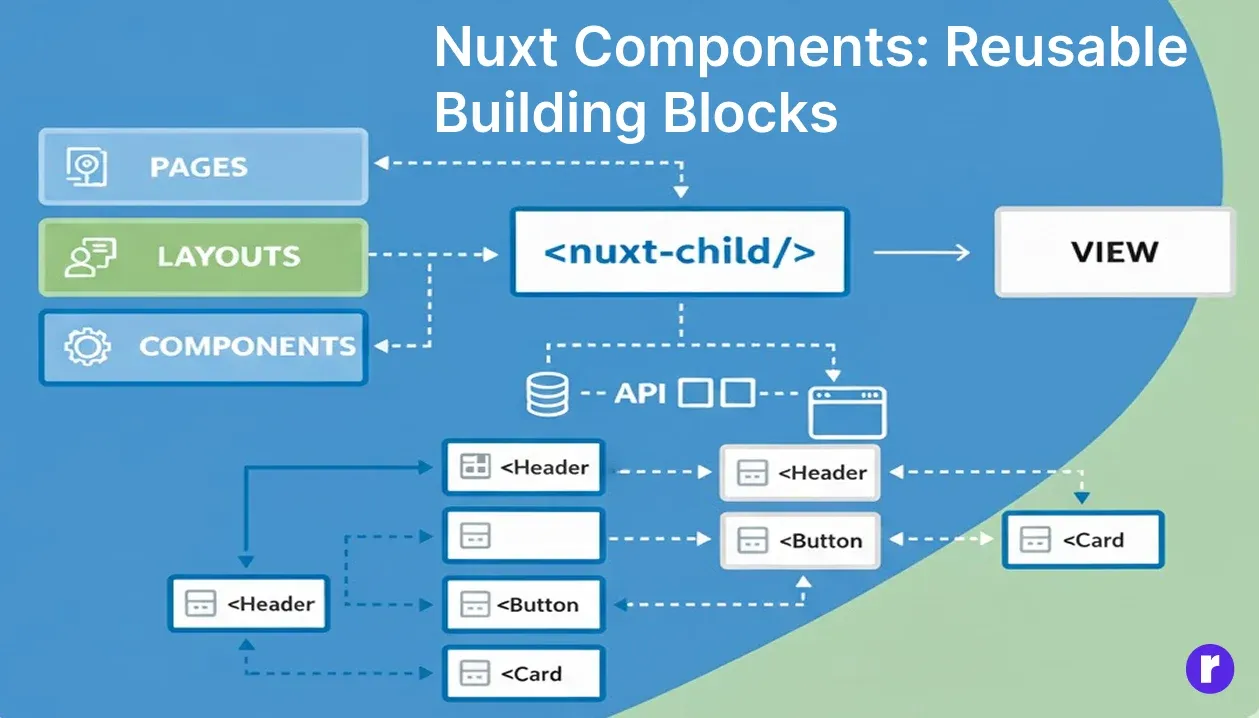
Components in Nuxt are reusable Vue components that can be used across pages and layouts. Components help maintain the DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principle in your codebase, making your app modular and easier to maintain.
Automatic Component Registration
Nuxt automatically scans the components/ directory and globally registers all Vue components found there, so you don't need to manually import them every time you want to use them.
Example directory structure:
components/
├── Navbar.vue
├── Footer.vue
└── Card.vue
You can then use these components directly in your pages or layouts without explicit imports:
<!-- pages/admin.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<Navbar />
<Card title="Welcome to Nuxt" description="This is a reusable card component." />
<Footer />
</div>
</template>
Benefits of Components
- Reusability: Write once, use anywhere throughout your app.
- Modularity: Each component is isolated, simplifying testing and debugging.
- Maintainability: Updating a component will automatically update all instances where it’s used.
- Cleaner Code: Break complex UIs into smaller, manageable building blocks.
Example Component:-
<!-- components/Card.vue -->
<template>
<div class="card">
<h2>{{ title }}</h2>
<p>{{ description }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
export default {
name: "Card",
props: {
title: String,
description: String
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.card {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
padding: 1rem;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
</style>
How Pages, Layouts, and Components Work Together
- Layouts provide the app’s structure.
- Pages populate layouts’ Nuxt slot.
- Components create reusable UI inside pages/layouts.
Example:-
- Default layout renders Navbar, Footer.
- index.vue rendered inside Nuxt .
- Pages use Card components for dynamic content.
Benefits: Clean architecture, scalability, maintainability.
Continue your learning journey at Radial Code .
Best Practices
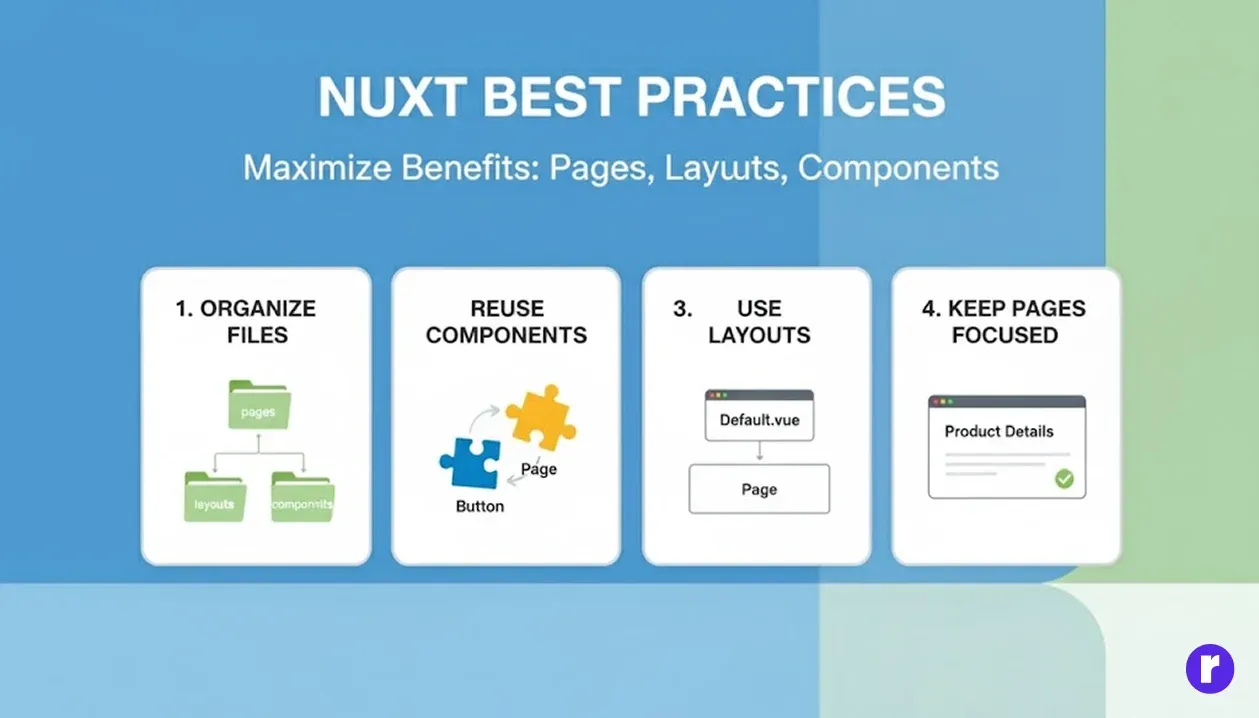
To maximize the benefits of Nuxt’s pages, layouts, and components, follow these best practices:
Organize Your Files
- Keep your pages/, layouts/, and components/ directories separate for clarity and maintainability.
- Use subdirectories within these folders to group related components or pages, making your project scalable and easier to navigate.
Reuse Components
- Avoid duplicating UI elements across pages by creating reusable components (e.g., buttons, cards, modals).
- Design generic, flexible components that can be customized via props.
Use Layouts Strategically
- Use the default layout for most common pages.
- Create specialized layouts for unique sections like dashboards landing pages, or authentication screens to maintain UX consistency.
Keep Pages Focused
- Pages should primarily handle content and page-specific logic.
- Avoid embedding layout or reusable component code directly inside pages to maintain separation of concerns.
Dynamic Routing with Pages
Nuxt’s file-based routing allows you to create dynamic routes easily using square bracket notation [param].
Example:-
<!-- pages/blog/[slug].vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h1>Blog Post: {{ slug }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
async asyncData({ params }) {
return { slug: params.slug }
}
}
</script>
This allows you to dynamically fetch data based on the route parameter, enabling you to build features like blogs or product pages efficiently.
